Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Engine Mount
Purpose, Function
-
The engine mount secures the engine and transaxle to the vehicle body, reducing vibration and noise.
Construction
-
The three points at the engine front (No.3 engine mount), one side of the transaxle (No.1 engine mount), and the rear upper part of the transaxle (No.4 engine mount) are supported.
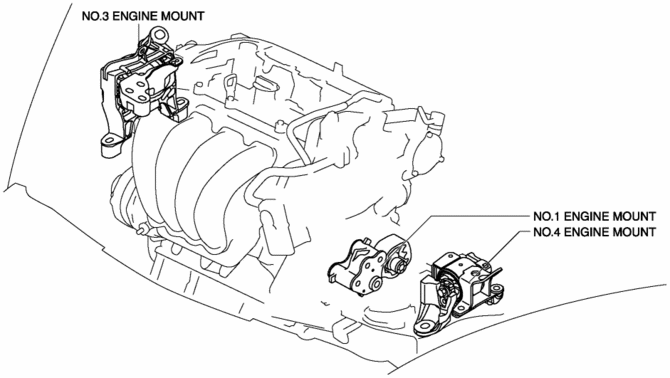
-
With the adoption of the oil-filled bushing type for the No.3 engine mount and No.4 engine mount rubber, the damper effect has been improved.
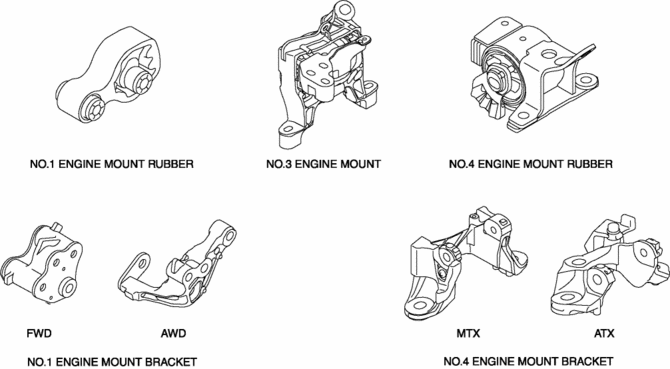
Operation
-
By locating the one side of the transaxle (No.1 engine mount) to the transaxle lower end, the No.1 engine mount absorbs the rotation force to the powertrain generated during engine torque fluctuation. The layout is designed to disperse the rotation force to the front/back directions of the engine.
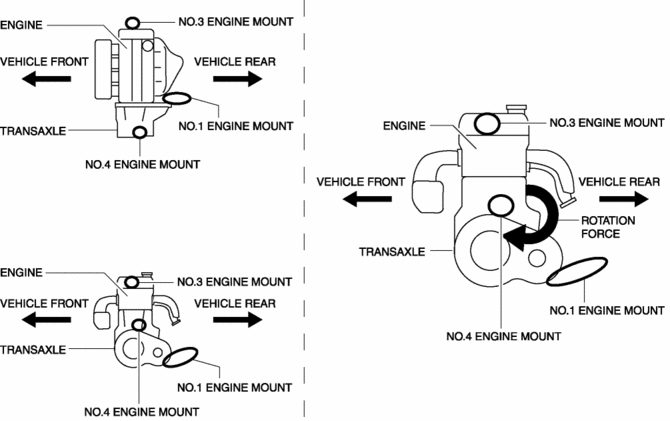
 Engine Mount Disassembly/Assembly
Engine Mount Disassembly/Assembly
No.1 Engine Mount (2WD)
1. Remove the front under cover No.2..
2. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
3. Install in the reverse order of removal.
1
No.1 engi ...
 Piston Assembly
Piston Assembly
...
Other materials:
Rain Sensor
Outline
The rain sensor detects the amount of rainfall and calculates the wiper operation
speed, and outputs a windshield wiper control signal to the front body control
module (FBCM) to perform automatic wiper operation (auto wiper system) according
to the amount of rainfall.
...
St 001/12 Special Service Tool Shipment January 2013
APPLICABLE MODEL(S)/VINS
2014 Mazda6
2014 CX-5
DESCRIPTION/PRICING
In support of the new 2014 Mazda6 and the 2014 CX-5, Mazda will ship to all dealers
one (1) new Special Service Tool (SST). The SST will be shipped automatically by
Mazda’s tool vendor, SPX during January 2013.
The followi ...
Cabin Side Frame Straight Line Dimensions [Dimensions]
Point symbol
Designation
Hole diameter or bolt or nut size mm {in}
A
Front side frame outer datum hole
?12 {0.47}
B
Front fender panel installation hole
?10 {0.39}
...
