Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Oil Pump
Outline
-
The oil pump has a mechanism for feedback control of oil pressure. As a result, an oil pressure increase of more than the set pressure is suppressed and oil pump drive resistance is reduced. In addition, because the set pressure can be changed (oil pressure two-step control) by operating the engine oil solenoid valve, the oil pump drive resistance is reduced even during low speed/low to medium loads.
Purpose, Function
-
The oil pump suctions the engine oil in the oil pan through the oil strainer and pumps engine oil into the engine.
Construction
-
The oil pump is installed on the lower part of the cylinder block (in oil pan).
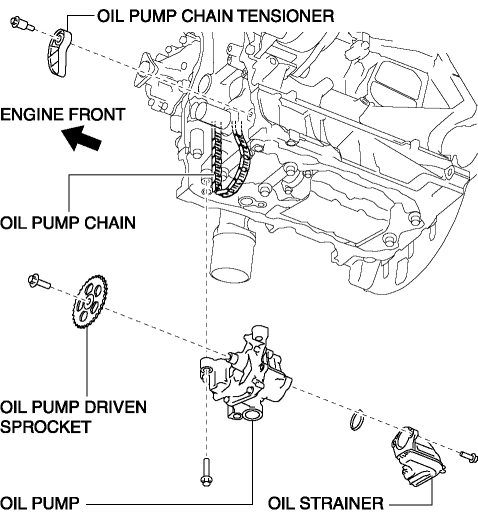
-
With the adoption of the chain drive type oil pump, the diameter of the rotor is reduced. As a result, the oil pump drive resistance has been reduced.
-
The oil pump consists of the following parts:
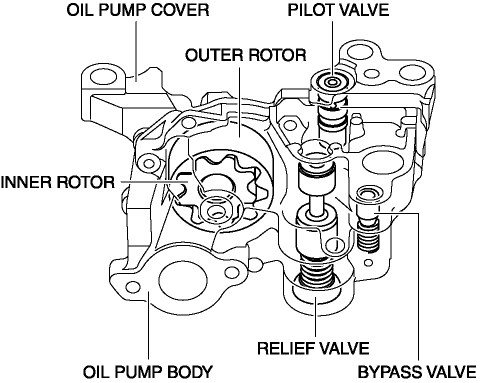
-
The relief valve and bypass valve is pushed and opened if oil pressure increases excessively when starting an extremely cold engine. As a result, the engine oil flows and excessive oil pressure increase is suppressed.
-
When the relief valve is pushed and opened, engine oil flows. As a result, the oil pressure decreases and the oil pump drive resistance is reduced.
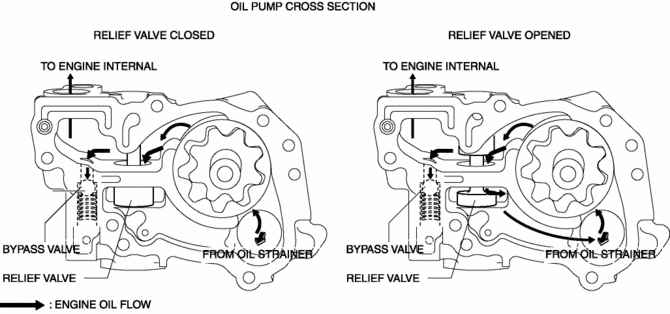
Operation
-
The oil pump adjusts oil pressure in two steps (low oil pressure setting, high oil pressure setting) by switching the oil passage with the operation of the engine oil solenoid valve. For the operation condition of the engine oil solenoid valve, refer to CONTROL SYSTEM..
-
When the engine oil solenoid valve is turned ON, oil pressure is also applied to the upper part of the pilot valve. Because the oil pressure applied to the upper and lower parts of the pilot valve is almost same, the pilot valve is pressed up by the spring force.
-
Oil pressure is applied to the upper part of the relief valve.
-
When oil pressure exceeds the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve is pressed down and engine oil flows. (oil pressure decrease)
-
When oil pressure is less than the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve closes. As a result, engine oil flowing stops (oil pressure increase).
-
Oil pressure is adjusted by repeating Step (c) to (d).
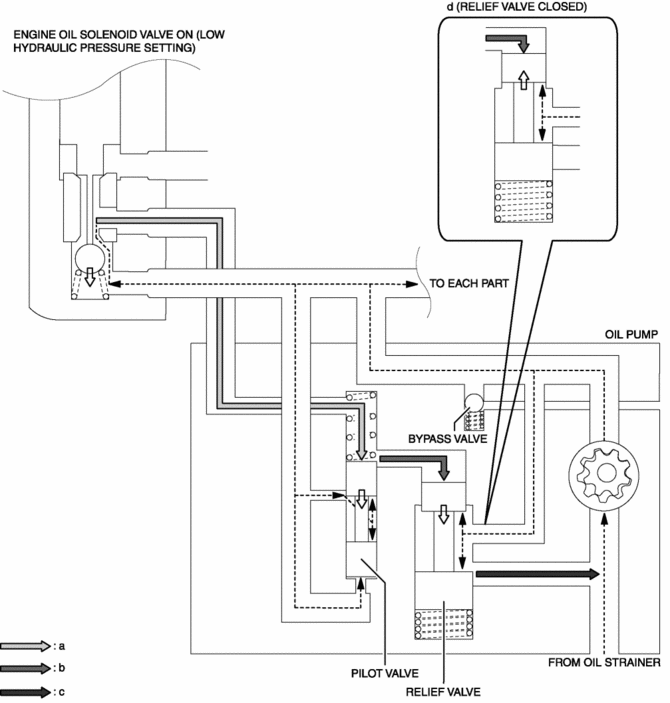
-
When oil pressure exceeds the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve is pressed up and oil pressure is applied to the upper part of the relief valve.
-
Because the relief valve opening pressure is exceeded by applying oil pressure to the upper part of the relief valve, the relief valve is pressed down and engine oil flows (oil pressure decrease).
-
When oil pressure is less than the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve closes. As a result, the relief valve closes and engine oil flow stops (oil pressure increase).
-
Oil pressure is adjusted by repeating Step (b) to (c).
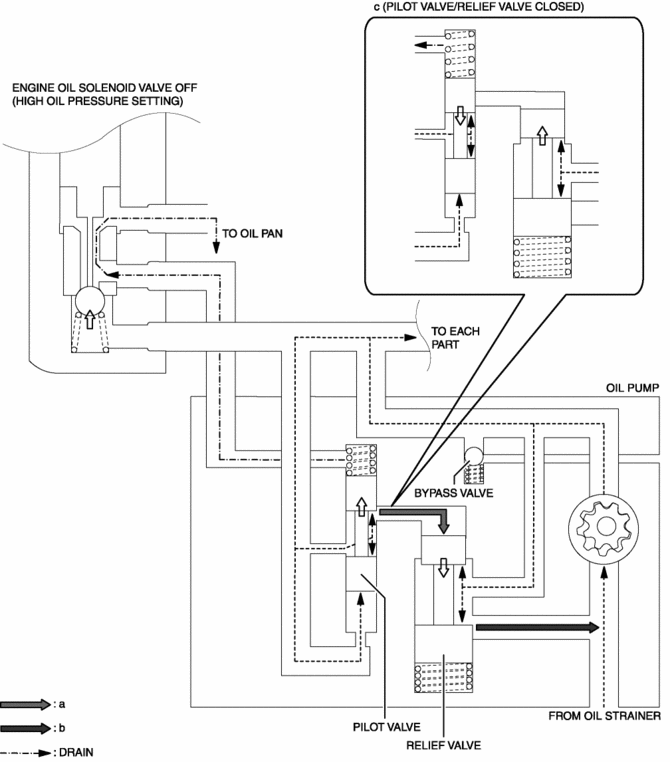
-
Engine oil flow when setting low oil pressure (engine oil solenoid valve
ON)
-
Engine oil flow when setting high oil pressure (engine oil solenoid valve
OFF)
 Oil Pump [Fw6 A EL, Fw6 Ax EL]
Oil Pump [Fw6 A EL, Fw6 Ax EL]
Purpose/Function
The oil pump generates hydraulic pressure in the oil line of the automatic
transaxle together with supplying lubrication to powertrain related parts.
Construction
...
 Oil Seal (Control Valve Body) Replacement [Fw6 A EL, Fw6 Ax EL]
Oil Seal (Control Valve Body) Replacement [Fw6 A EL, Fw6 Ax EL]
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
2. Remove the air cleaner component..
3. Disconnect the control valve body connector.
CAUTION:
Make sure that your hand does not touch the ...
Other materials:
Hood Latch Switch Inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
2. Remove the front bumper..
3. Disconnect the hood latch switch connector..
4. Verify that the continuity is as indicated in the table.
NOTE:
Inspect the continuity when the hood is open and closed.
If the operation as i ...
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
Purpose, Outline
The tire pressure monitoring system monitors the tire pressure of all 4 tires.
If the tire pressure of 1 tire or more becomes excessively low, the driver is
notified.
A tire pressure monitoring system has been adopted which indirectly inspects
the tire pres ...
Tire Pressure Monitoring System Set Switch
Purpose
The tire pressure monitoring system set switch is used to initialize the
tire pressure monitoring system.
Construction, Operation
The tire pressure monitoring system set switch is installed to the instrument
panel.
The tire pressure monitoring sy ...
