Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Miller Cycle Engine
Outline
-
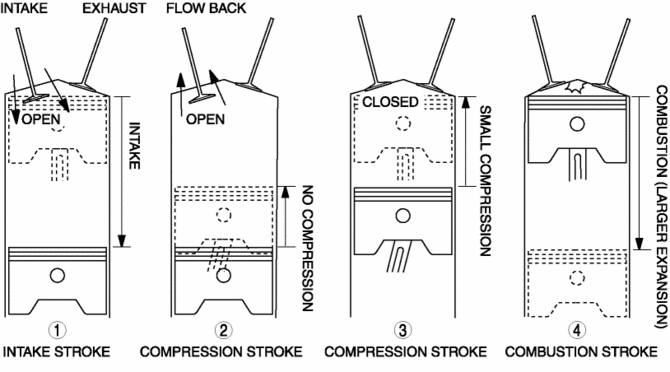
The Miller cycle engine is a high-efficiency engine which achieves high fuel economy performance by obtaining a high-expansion ratio.
-
The Miller cycle engine achieves a high-expansion ratio without increasing its effective compression ratio by retarding the intake air valve close timing.
Operation
1. Intake air is introduced into the cylinder.
2. The intake valve is kept open after the intake stroke is finished to force the air in the cylinder to flow back to the intake pipe.
3. The compression stroke starts from the position in which the intake valve is closed (small compression).
4. The air-fuel mixture is combusted and the piston is pushed down to BDC (large expansion).
 Mechanical
Mechanical
Outline
The sliding resistance*1 has been reduced by:
the adoption of a rocker arm (built into needle roller bearing)
reducing load on the valve spring
narrow ...
 Non Return Valve Inspection
Non Return Valve Inspection
WARNING:
Fuel is very flammable liquid. If fuel spills or leaks from the pressurized
fuel system, it will cause serious injury or death and facility breakage. Fuel
can also irritate skin ...
Other materials:
Passenger Compartment Temperature Sensor [Full Auto Air Conditioner]
Purpose
The passenger compartment temperature sensor detects the cabin temperature.
Function
The passenger compartment temperature sensor converts the detected temperature
to an electric signal.
Construction
A thermistor-type passenger compartment temperature sens ...
Air Intake Control [Full Auto Air Conditioner]
Purpose
The air intake control switches the air intake port (FRESH/REC) according
to the vehicle environment.
Function
The air intake control drives the air intake actuator and switches the air
intake door position according to the operations of the REC, FRESH and defroster ...
Fuel Pump Control Module Inspection
1. Perform the KOEO self-test..
2. Verify that a fuel pump control module related DTC is detected..
If DTCs are detected, repair the malfunctioning part according to the applicable
DTC troubleshooting..
If a DTC is not detected, go to the next step.
3. Inspect the followin ...
