Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Starter Inspection [Skyactiv G 2.0]
On-vehicle Inspection
1. Verify that the battery is fully charged.
2. The starter is normal if it rotates smoothly and without any noise when the engine is cranked.
-
If the starter does not operate, inspect the following:
-
Remove the starter, and inspect the starter unit.
-
Inspect the related wiring harnesses, the ignition switch, and the transaxle range switch (ATX) or starter interlock switch (MTX).
No-load Test
1. Verify that the battery is fully charged.
2. Connect the starter, battery, and a tester as shown in the figure.
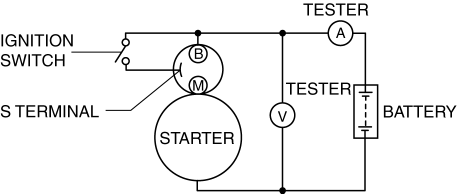
3. Operate the starter and verify that it rotates smoothly.
-
If the starter does not rotate smoothly, inspect the starter unit.
4. Measure the voltage and current while the starter is operating.
-
If not within specification, replace the starter.
-
Starter no-load test voltage
-
11 V
-
Starter no-load test current
-
95 A or less
Magnetic Switch Operation Inspection
Pull-out test
NOTE:
-
Depending on the battery charge condition, the starter motor pinion may rotate while in an extended state. This is due to current flowing to the starter motor through the pull-in coil to turn the starter motor, and does not indicate an abnormality.
1. Verify that the starter motor pinion is extended while battery positive voltage is connected to terminal S and the starter body is grounded.
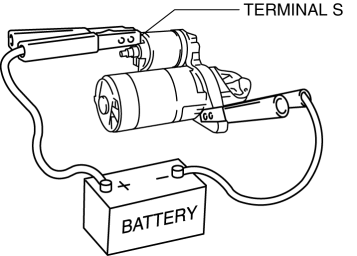
-
If the starter motor pinion is not extended, repair or replace the starter.
Return test
1. Disconnect the motor wire from terminal M.
2. Connect battery positive voltage to terminal M and ground the starter body.
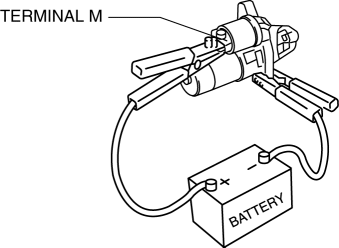
3. Pull out the drive pinion with a screwdriver. Verify that it returns to its original position when released.
-
If it does not return, repair or replace the starter.
Pinion Gap Inspection
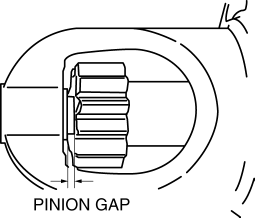
1. Pull out the drive pinion with the battery positive voltage connected to terminal S and the starter body grounded.

CAUTION:
-
Applying power for more than 10 s can damage the starter. Do not apply power for more than 10 s.
2. Measure the pinion gap while the drive pinion is extended.
-
If not as specified, adjust with an adjustment washer (between drive housing front cover and magnetic switch).
-
Starter pinion gap
-
0.5—2.0 mm {0.02—0.07 in}
Starter Inner Parts Inspection
Armature
1. Verify that there is no continuity between the commutator and the core at each segment using a tester.
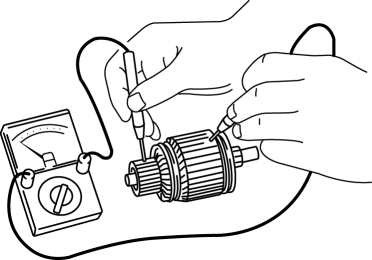
-
If there is continuity, replace the armature.
2. Verify that there is no continuity between the commutator and the shaft using a tester.
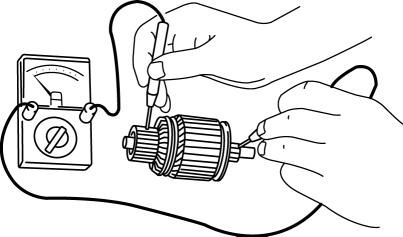
-
If there is continuity, replace the armature.
3. Place the armature on V?blocks, and measure the runout using a dial indicator.
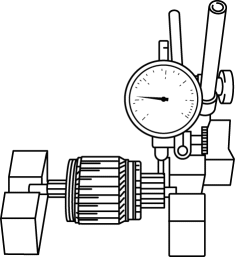
-
If not within specification, replace the armature.
-
Starter armature runout
-
0.1 mm {0.004 in} max.
4. Measure the commutator diameter.
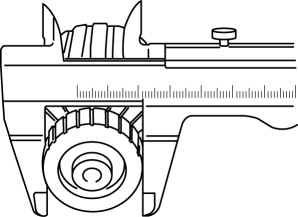
-
If not within the minimum specification, replace the armature.
-
Starter commutator diameter
-
Standard: 29.4 mm {1.16 in}
-
Minimum: 28.8 mm {1.13 in}
5. Measure the segment groove depth of the commutator.
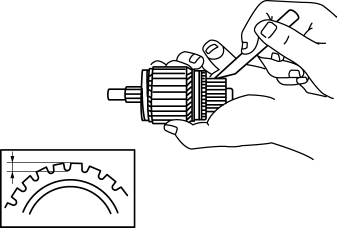
-
If not within the minimum specification, undercut the grooves to the standard depth.
-
Segment groove depth of starter commutator
-
Standard: 0.5 mm {0.02 in}
-
Minimum: 0.2 mm {0.008 in}
Magnetic switch
1. Inspect for continuity between terminals S and M using a tester.
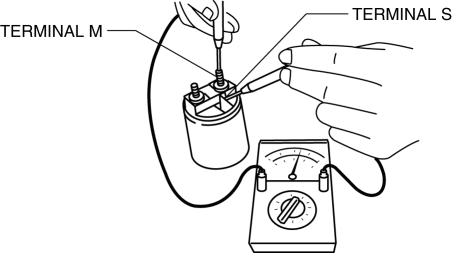
-
If there is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
2. Inspect for continuity between terminal S and the body using a tester.
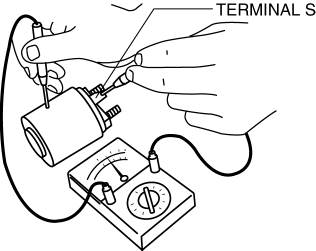
-
If there is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
3. Verify that there is no continuity between terminals M and B using a tester.
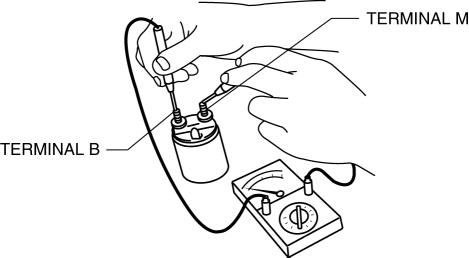
-
If there is continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
Brush and brush holder
1. Verify that there is no continuity between each insulated brush and plate using a tester.
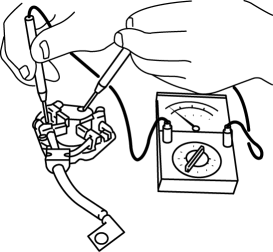
-
If there is continuity, replace the brush holder.
2. Measure the brush length.
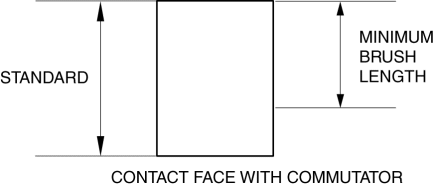
-
If any brush is worn almost to or beyond the minimum specification, replace all of the brushes.
-
Starter brush length
-
Standard: 12.3 mm {0.484 in}
-
Minimum: 5.5 mm {0.22 in}
3. Measure the brush spring force using a spring balance.
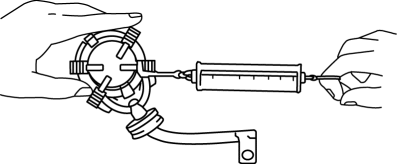
-
If not within the minimum specification, replace the brush and brush holder component.
-
Starter brush spring force
-
Standard: 15.1—20.4 N {1.54—2.08 kgf, 3.40—4.58 lbf}
-
Minimum: 2.75 N {0.280 kgf, 0.618 lbf}
 Starter Disassembly/Assembly [Skyactiv G 2.0]
Starter Disassembly/Assembly [Skyactiv G 2.0]
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2. Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
1
Magnetic switch
2
Adjustment washer
...
 Starter Interlock Switch Inspection [Skyactiv G 2.0]
Starter Interlock Switch Inspection [Skyactiv G 2.0]
CAUTION:
Do not reuse the starter interlock switch if it is removed from the vehicle
even once. Replace with a new starter interlock switch when installing.
1. Disconnect the negative ...
Other materials:
Quick Release Connector (Emission System) Removal/Installation
Quick Release Connector Type and Position
CAUTION:
Verify the type and location, and install/remove properly.
U.S.A. and CANADA
Except U.S.A. and CANADA
Type A Removal
CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the evaporative pipe when unlocking the retainer.
NOTE:
...
Instrumentation/Driver Info.
Outline
An LCD has been adopted to the instrument cluster which displays the ambient
temperature, trip computer, and odometer/tripmeter.
A blind spot monitoring (BSM) system has been adopted which notifies the
driver of vehicles approaching from behind on the left or right adjac ...
Refrigerant System Service Cautions
Handling Insufficient Refrigerant Level
If an insufficient refrigerant level is detected at troubleshooting, do
not charge (add) the refrigerant. Because an accurate amount of refrigerant
cannot be determined from the pressure indicated on the manifold gauge, never
charge the refrige ...
