Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: ABS Control
Outline
-
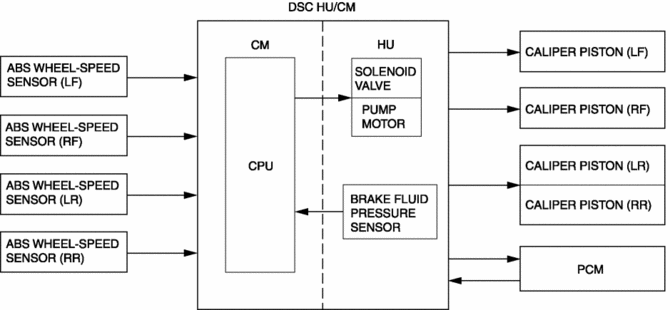
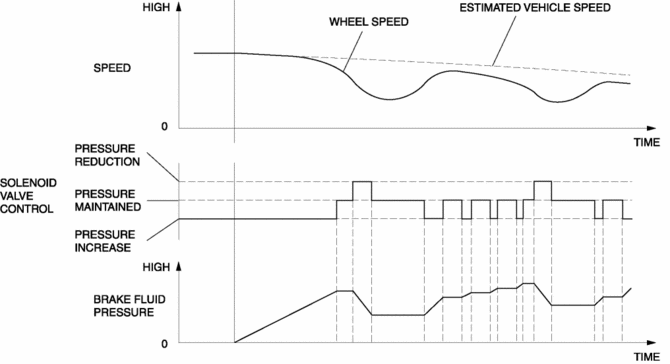
ABS control occurs when wheel slip is determined by the DSC CM (based on the four ABS wheel-speed sensors). Then, the DSC HU inlet and outlet solenoid valves are operated and brake fluid pressure is controlled accordingly to prevent wheel lock-up.
Feature
-
Use of ABS control during emergency braking or on slippery road surfaces allows directional stability to be maintained, steerability ensured, and stopping distance to be reduced.
-
The ABS control system has independent front wheel control and unified control (select low) for the rear wheels.
NOTE:
-
Select low control: A control system in which the left and right vehicle wheel speeds are compared and brake fluid pressure is controlled according to the wheel most likely to lock-up.
-
Construction
Block Diagram
Operation
-
When the DSC CM determines wheel slip conditions based on the signals from the ABS wheel-speed sensors during braking, the DSC CM operates the DSC HU inlet and outlet solenoid valves, reducing and maintaining brake fluid pressure in accordance with the wheel slip factors. Then, when the wheel slip condition has passed, brake fluid pressure is increased and maintained, ensuring braking with a constantly stable brake force.
Control condition transition diagram
 ABS
ABS
...
 ABS Wheel Speed Sensor And ABS Sensor Rotor
ABS Wheel Speed Sensor And ABS Sensor Rotor
Purpose/Function
The ABS wheel-speed sensor and ABS sensor rotor detect the rotation condition
of each wheel and transmit this information to the DSC HU/CM.
The signal from the ABS w ...
Other materials:
Overheating
Overheating
If the High engine coolant temperature warning light illuminates, the vehicle
loses power, or you hear a loud knocking or pinging noise, the engine is probably
too hot.
WARNING
Switch the ignition to off and make sure the fan is not running before attempting
to work near the c ...
Fuel Injector Inspection
Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
2. Remove the plug hole plate..
3. Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
4. Inspect the resistance between fuel injector terminals A and B.
Fuel injector resistance
1.74—2.04 ohms [20 °C {68 °F}]
...
Rain Sensor
Outline
The rain sensor detects the amount of rainfall and calculates the wiper operation
speed, and outputs a windshield wiper control signal to the front body control
module (FBCM) to perform automatic wiper operation (auto wiper system) according
to the amount of rainfall.
...
