Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Engine Oil Control
Outline
-
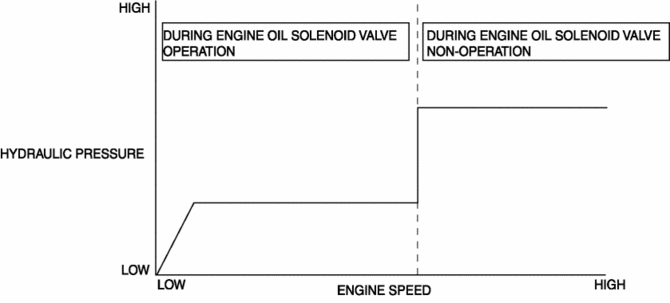
The PCM reduces the oil pump load applied to the engine by controlling the appropriate engine hydraulic pressure according to the engine operation conditions.
-
The engine hydraulic pressure switches in two steps. When hydraulic pressure is not needed, the oil pump discharge amount is reduced by the operation of the engine oil solenoid valve.
Block Diagram

Operation
-
The PCM switches the engine oil pressure which lubricates the engine in two steps by driving the engine oil solenoid valve according to the engine operation conditions.
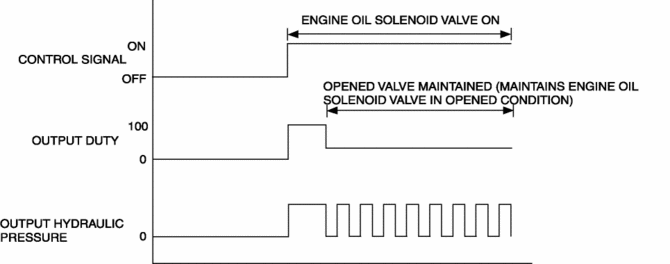
Output duty value determination
-
The PCM controls the operational voltage energized to the engine oil solenoid according to the duty signal. After opening the engine oil solenoid valve at the output duty ratio of 100%, load applied to the parts is reduced by lowering the duty value to the output duty value at which the open valve condition can be maintained. The output duty value for maintaining the opening value changes according to the battery voltage.
Engine oil solenoid valve operation conditions
-
The PCM operates the engine oil solenoid valve when all of the following conditions is met:
-
Engine speed: Less than 4,000 rpm
-
Engine coolant temperature: Less than 98 °C {208 °F}
-
Charging efficiency: Less than specification (varies according to engine speed.)
-
For details on the engine oil solenoid valve, refer to the LUBRICATION SYSTEM..
Hydraulic pressure switching mechanism
-
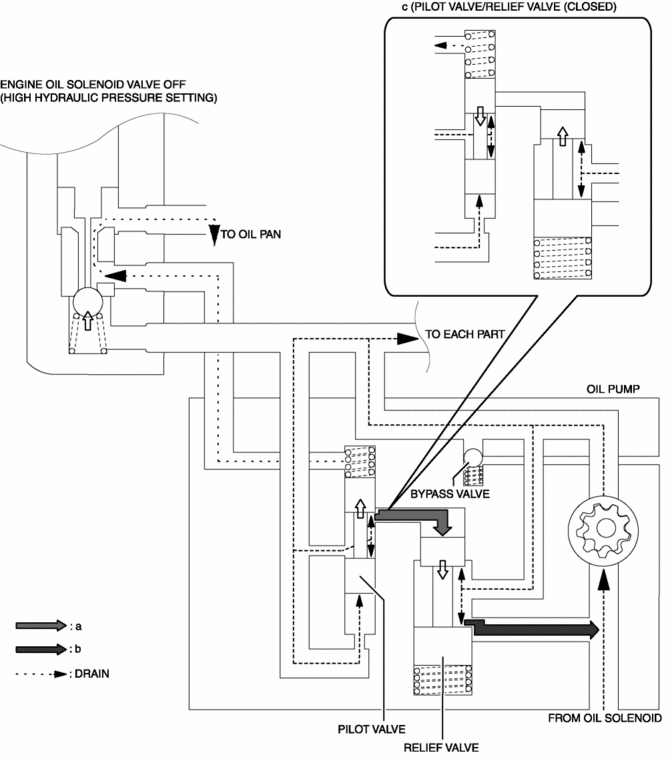
When the engine oil solenoid valve operates, the hydraulic circuit changes according to the following. The engine oil supply amount is controlled by changing the hydraulic circuit.
-
When the engine oil solenoid valve turns on, hydraulic pressure is also applied to the top of the pilot valve. The pilot valve presses downward by spring force because the hydraulic pressure applied to the top and bottom of the pilot valve is nearly equal.
-
Hydraulic pressure is applied to the top of the relief valve.
-
When the hydraulic pressure exceeds the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve is pressed downward and engine oil flows out (Hydraulic pressure decrease).
-
When the hydraulic pressure is less than the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve closes. As a result, engine oil outflow stops (Hydraulic pressure increase).
-
(c)-(d) is performed repeatedly to adjust the hydraulic pressure.
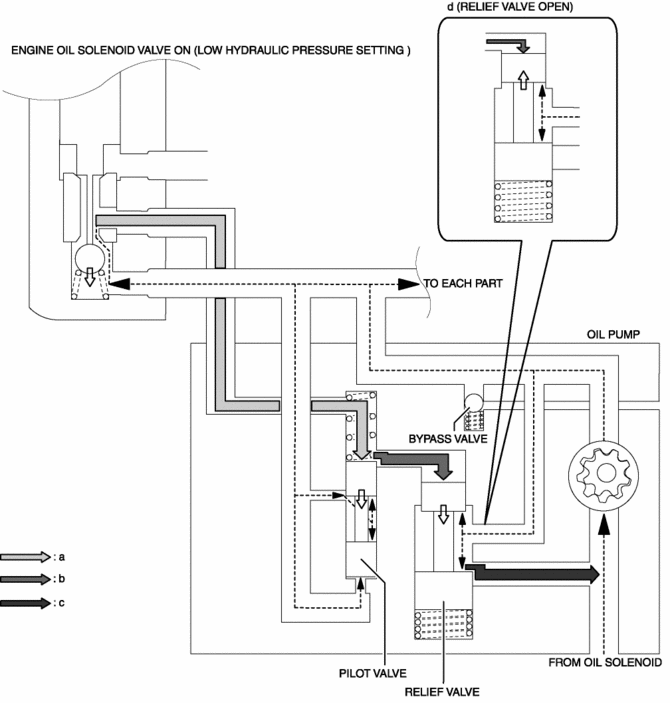
-
When the hydraulic pressure exceeds the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve is pressed upward and hydraulic pressure is applied.
-
Because the hydraulic pressure exceeds the relief valve opening pressure by the hydraulic pressure applied to the top of the relief valve, the relief valve is pressed downward and engine oil flows out (Hydraulic pressure decrease).
-
When the hydraulic pressure is less than the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve closes. As a result, the relief valve is closed and engine oil outflow stops (Hydraulic pressure increase).
-
(a)-(c) is performed repeatedly to adjust the hydraulic pressure.
-
Engine oil flow during low hydraulic pressure setting (engine oil solenoid
valve ON)
-
Engine oil flow during high hydraulic pressure setting (engine oil solenoid
valve OFF)
 Lubrication
Lubrication
...
 Engine Oil Level Inspection
Engine Oil Level Inspection
1. Position the vehicle on level ground.
2. Warm up the engine.
3. Stop the engine and allow at least 5 min before continuing.
4. Remove the dipstick, wipe it cleanly, and reinstall it fully.
...
Other materials:
Front Seat Belt Removal/Installation
WARNING:
Handling the front seat belt (pre-tensioner seat belt) improperly can accidentally
deploy the pre-tensioner seat belt, which may seriously injure you. Read the
air bag system service warnings and cautions before handling the front seat
belt.
(See AIR BAG SYSTEM SERVICE W ...
Transaxle Fluid Temperature (Tft) Sensor [Fw6 A EL, Fw6 Ax EL]
Purpose/Function
The transaxle fluid temperature (TFT) sensor detects the ATF temperature
in the oil pan.
The transaxle fluid temperature (TFT) sensor signal is used for automatic
shift control, TCC control, line pressure control, direct electric shift control,
learning contr ...
Tire Pressure Monitoring System Initialization Procedure
Perform the tire pressure monitoring system initialization when the following
operations have been performed:
Tire pressures have been adjusted
Tires or wheels have been replaced
Tires have been rotated
DSC HU/CM replaced
DSC HU/CM ...
