Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Engine Mount
Purpose, Function
-
The engine mount secures the engine and transaxle to the vehicle body, reducing vibration and noise.
Construction
-
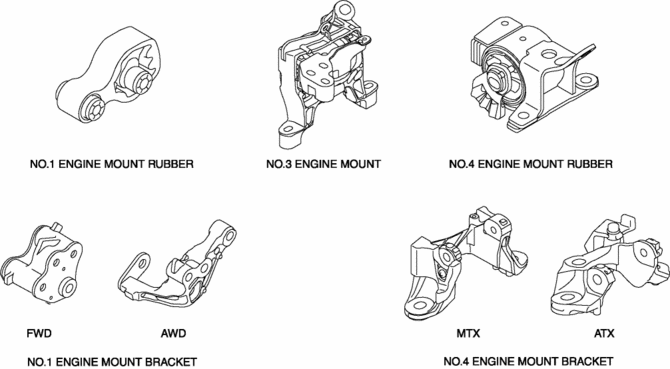
The three points at the engine front (No.3 engine mount), one side of the transaxle (No.1 engine mount), and the rear upper part of the transaxle (No.4 engine mount) are supported.
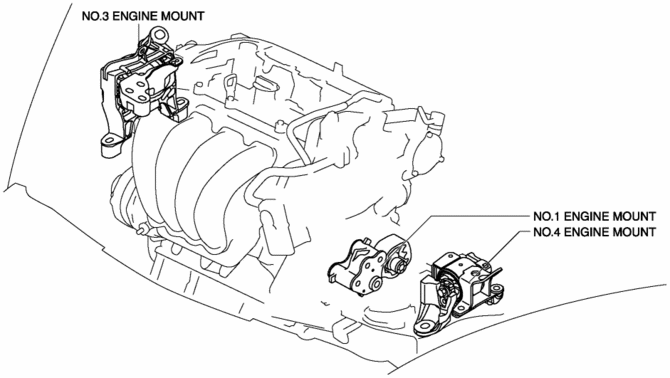
-
With the adoption of the oil-filled bushing type for the No.3 engine mount and No.4 engine mount rubber, the damper effect has been improved.
Operation
-
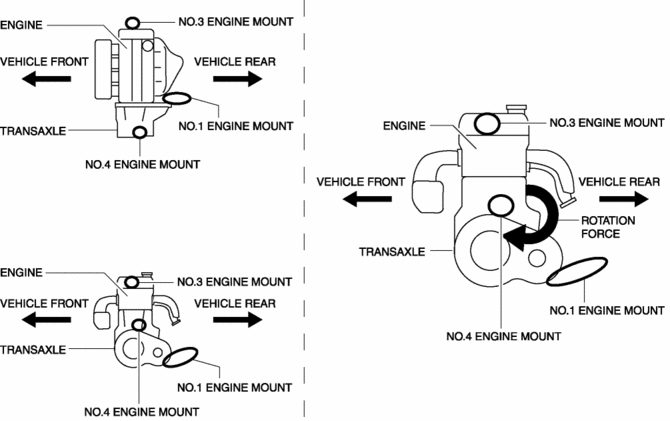
By locating the one side of the transaxle (No.1 engine mount) to the transaxle lower end, the No.1 engine mount absorbs the rotation force to the powertrain generated during engine torque fluctuation. The layout is designed to disperse the rotation force to the front/back directions of the engine.
 Engine Mount Disassembly/Assembly
Engine Mount Disassembly/Assembly
No.1 Engine Mount (2WD)
1. Remove the front under cover No.2..
2. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
3. Install in the reverse order of removal.
1
No.1 engi ...
 Piston Assembly
Piston Assembly
...
Other materials:
Pre Delivery Inspection
Pre?Delivery Inspection Table
Exterior
INSPECT and ADJUST, if necessary, the following items to specification:
?Glass, exterior bright metal and paint for damage
?Wheel lug nuts
?All weatherstrips for damage or detachment
?Adjust tire pressures to specification
Adjust the tire pr ...
Front Power Window Regulator Removal/Installation
1. Perform the front door glass preparation..
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
3. Remove the following parts:
a. Inner garnish.
b. Front door trim.
c. Front door glass.
d. Front door speaker.
e. Front power window motor.
4. Remove bolt A.
5. Remove nuts B.
6. Insert ...
Headliner
Purpose/Function
The headliner is equipped with a shock absorbing pad for driver's head protection
during a collision.
Construction
The front and rear side of the headliner is equipped with a shock absorbing
pad with a plastic rib-pad structure.
...
