Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Evaporator
Purpose
-
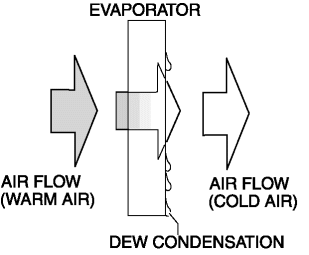
The evaporator cools the passing air.
Function
-
The evaporator vaporizes the atomized refrigerant flowing internally, and the air passing through the evaporator is cooled by the release of latent heat. The moisture in the air is condensed at this time and dehumidified air is blown into the cabin.
Construction
-
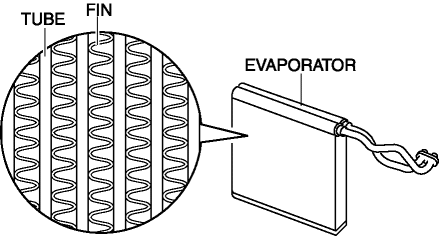
The evaporator consists of the tube which passes refrigerant, and the heat radiation fin.
-
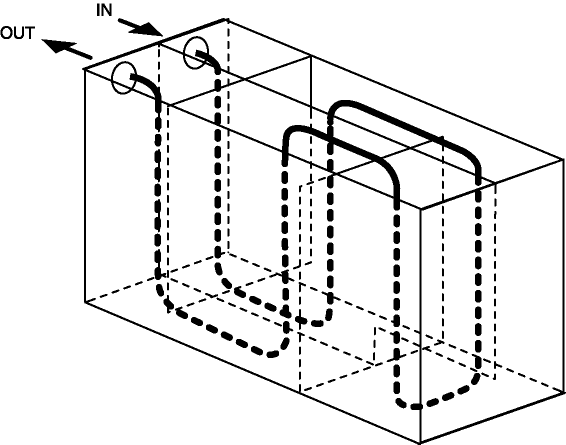
The cooling medium flow pattern shown in the figure has been adopted for the evaporator.
Operation
-
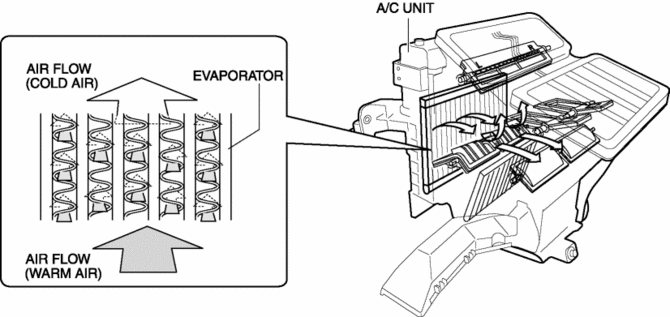
The atomized refrigerant sent from the expansion valve is captured by heat from the outside. As a result, the evaporator is cooled.
-
The air blown by the blower motor is cooled by heat exchange when it passes the heat radiation fin of the heater core.
Fail-safe
-
Function not equipped.
 Drive Belt [Skyactiv G 2.0]
Drive Belt [Skyactiv G 2.0]
Purpose, Function
The drive belt transmits rotation force of the crankshaft pulley to the pulley
for the auxiliary parts.
Construction
The drive belt is installed to the front o ...
 Evaporator Inspection
Evaporator Inspection
1. Inspect the evaporator for damage, cracks, and oil leakage.
If there is any malfunction, replace the evaporator.
2. Visually inspect the fins for bending.
If there is any bend ...
Other materials:
Oil Pan
Purpose, Function
The engine oil required for lubrication in the engine accumulates in the
oil pan.
Construction
The oil pan is installed on the lower part of the cylinder block.
Silicone sealant with excellent sealing has been adopted for the oil pan
gask ...
Power Window Main Switch
Purpose
Remote control of door glass open/close and power outer mirror adjustment
are possible with occupant seated in the cabin.
Function
Power window main switch
Manual
When the power window main switch is operated for manual open/close operation,
it sends ...
Bsm Indicator Light Flashes While Not Under Bsm Indicator Light Flashing Conditions
(No Combination Switch Operation (Turn Signal Switch)) [Blind Spot Monitoring (Bsm)]
Description
BSM indicator light flashes while not under BSM indicator light-flashing
conditions (no combination switch operation (turn signal switch)
The BSM indicator light flashes despite not satisfying the BSM indicator
light flashing ...
