Mazda CX-5 Service & Repair Manual: Steering Column And Shaft
Purpose/Function
-
The steering input force, generated when the driver operates the steering wheel, is transmitted to the steering gear.
Construction
-
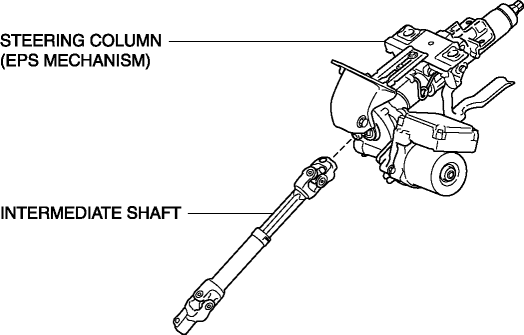
The steering column and shaft consists of the steering column with a built-in EPS mechanism and the intermediate shaft.
-
As a result of impact absorbing mechanisms on the steering column and intermediate shaft, when a collision occurs, the steering shaft effectively absorbs the impact energy that would be transmitted to the driver, thereby reducing injury.
-
Due to the adoption of a tilt/telescope mechanism for the steering shaft on all vehicles, operability has been improved.
Operation
-
EPS mechanism
-
Based on the steering torque signal from the torque sensor and the vehicle speed and engine speed signals from the PCM, the EPS CM drives the EPS motor and transmits the assist torque to the intermediate shaft via the deceleration mechanism.
-
Energy absorbing system
-
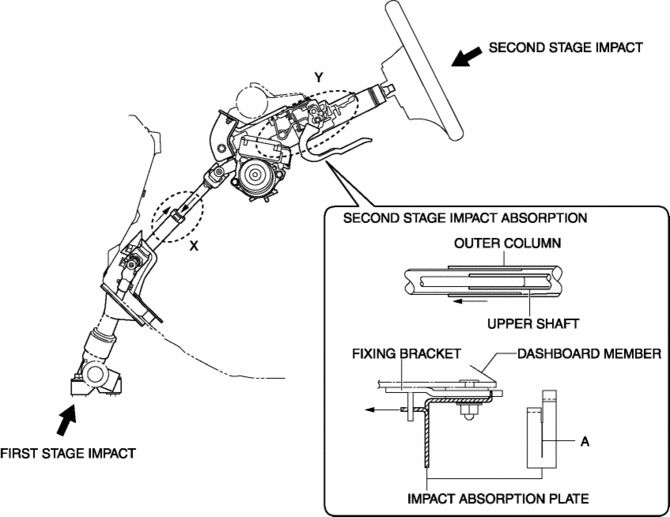
At the moment of a collision, when impact energy (first stage impact) is input from the vehicle front due to the rearward collapse of the steering gear, the intermediate shaft contracts to absorb the impact from the driver. (Section X in the figure)
-
When the body of the driver contacts the steering wheel (second stage impact), the fixing bracket comes off the dashboard member, and the upper shaft and the outer column slide forward. At this time, the impact absorption plate (one part secured to instrument panel member, another part to fixing bracket) deforms (area A shown in figure cracks) to absorb the impact to the driver. (Section Y in the figure)
-
Tilt/telescope mechanism
-
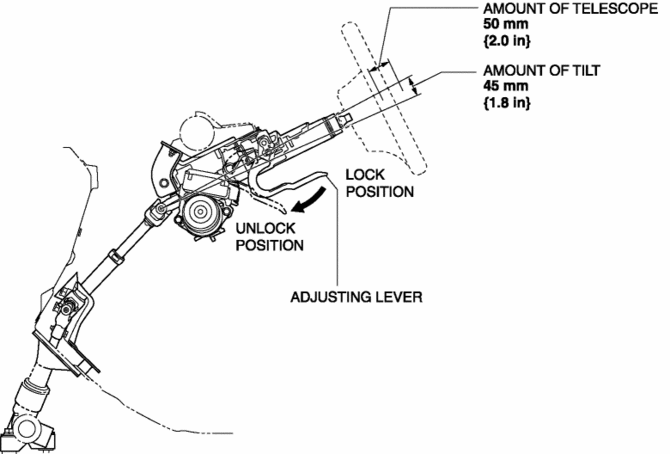
The steering wheel can be moved in the up/down and forward/backward direction when the adjusting lever is pressed towards the front of the vehicle to release the lock of the tilt/telescope system.
-
The tilt/telescope mechanism has a movement range of 45 mm {1.8 in}
(tilt)/ 50 mm {2.0 in}
(telescope) and can be adjusted, without steps, to anywhere in this range.
Fail-safe
-
Function not equipped.
 Wheel, Column
Wheel, Column
...
 Steering Shaft Inspection
Steering Shaft Inspection
1. Inspect the steering column for excessive play and damage.
2. Verify that the clearance between the projection on the steering column shown
in the figure and the bracket is less than 2.0 mm {0. ...
Other materials:
Intake Air Temperature (Iat) Sensor
IAT Sensor No.1
Purpose/Function
Detects the IAT before it passes through the throttle body as basic information
for mainly determining the fuel injection amount.
Detects the IAT before it passes through the throttle body and inputs it
to the PCM as an IAT signal.
Constru ...
Liftgate Removal/Installation
WARNING:
Removing the stay damper, liftgate hinge securing bolt, or liftgate without
supporting the liftgate may cause the liftgate to fall off and injure you. When
removing the stay damper, liftgate hinge, or liftgate, always use two persons
to perform the work.
1. Disconnect ...
Rear Trailing Link Removal/Installation
1. Remove the floor under cover..
2. Disconnect the rear parking cable..
3. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
4. Install in the reverse order of removal.
5. Inspect the wheel alignment and adjust it if necessary..
1
Rear trailing link installatio ...
